Space Weather Observations, Alerts, and Forecast
Instruments on board the NOAA Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite (POES) continually monitor the power flux carried by the protons and electrons that produce aurora in the atmosphere. SWPC has developed a technique that uses the power flux observations obtained during a single pass of the satellite over a polar region (which takes about 25 minutes) to estimate the total power deposited in an entire polar region by these auroral particles. The power input estimate is converted to an auroral activity index that ranges from 1 to 10.
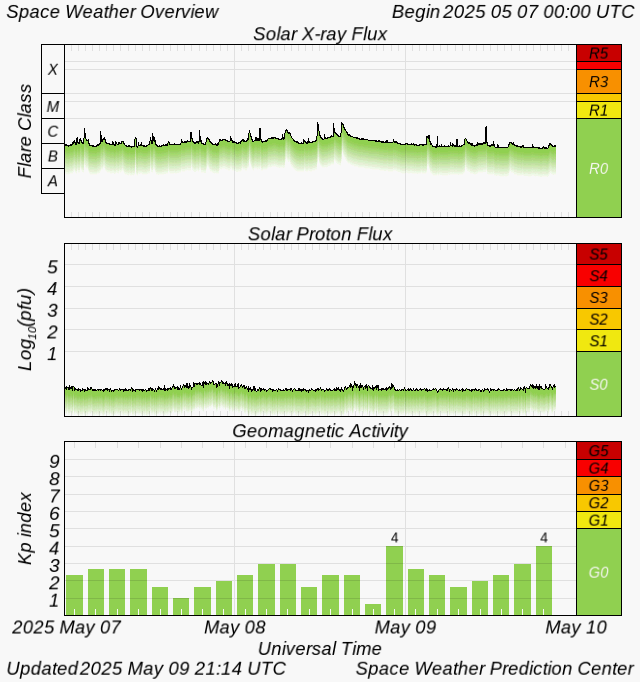
Current Space Weather Overview
|
3-day Solar-Geophysical Forecast
Product: 3-Day Forecast
- Issued: 2025 Dec 18 0030 UTC
Prepared by the U.S. Dept. of Commerce, NOAA, Space Weather Prediction Center.
Geomagnetic Activity Observation and Forecast
The greatest observed 3 hr Kp over the past 24 hours was 4.67 (NOAA Scale G1). The greatest expected 3 hr Kp for Dec 18-Dec 20 2025 is 4.67 (NOAA Scale G1).
| Dec 18 | Dec 19 | Dec 20 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 00-03UT | 4.00 | 3.00 | 2.67 |
| 03-06UT | 4.67 (G1) | 3.00 | 2.67 |
| 06-09UT | 4.00 | 2.67 | 2.33 |
| 09-12UT | 2.67 | 2.00 | 1.67 |
| 12-15UT | 2.33 | 1.67 | 1.67 |
| 15-18UT | 2.00 | 1.33 | 1.33 |
| 18-21UT | 2.33 | 1.33 | 2.00 |
| 21-00UT | 3.00 | 2.67 | 2.00 |
Rationale: G1 (Minor) geomagnetic storms are expected on 18 Dec due to persistent CH HSS influence.
Solar Radiation Activity Observation and Forecast
Solar radiation, as observed by NOAA GOES-18 over the past 24 hours, was below S-scale storm level thresholds.
| Dec 18 | Dec 19 | Dec 20 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 or greater | 1% | 1% | 1% |
Rationale: No S1 (Minor) or greater solar radiation storms are expected. No significant active region activity favorable for radiation storm production is forecast.
Radio Blackout Activity and Forecast
No radio blackouts were observed over the past 24 hours.
| Dec 18 | Dec 19 | Dec 20 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1-R2 | 15% | 15% | 15% |
| R3 or greater | 1% | 1% | 1% |
Rationale: No R1 (Minor) or greater radio blackouts are expected. No significant active region flare activity is forecast.
Solar Wind
Real-Time Solar Wind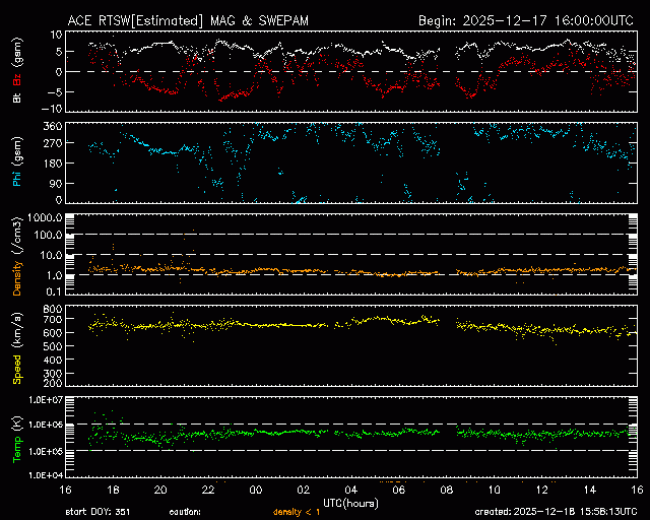
Real-Time Solar Wind data broadcast from NASA's ACE satellite. |
|
WSA-Enlil Solar Wind Prediction |
| Move your cursor over the timeline to 'scrub' through the forecast. |
WSA-Enlil is a large-scale, physics-based prediction model of the heliosphere, used by the Space Weather Forecast Office to provide 1-4 day advance warning of solar wind structures and Earth-directed coronal mass ejections (CMEs) that cause geomagnetic storms. Solar disturbances have long been known to disrupt communications, wreak havoc with geomagnetic systems, and to pose dangers for satellite operations.
Solar Cycle
Sun Spot Number Progression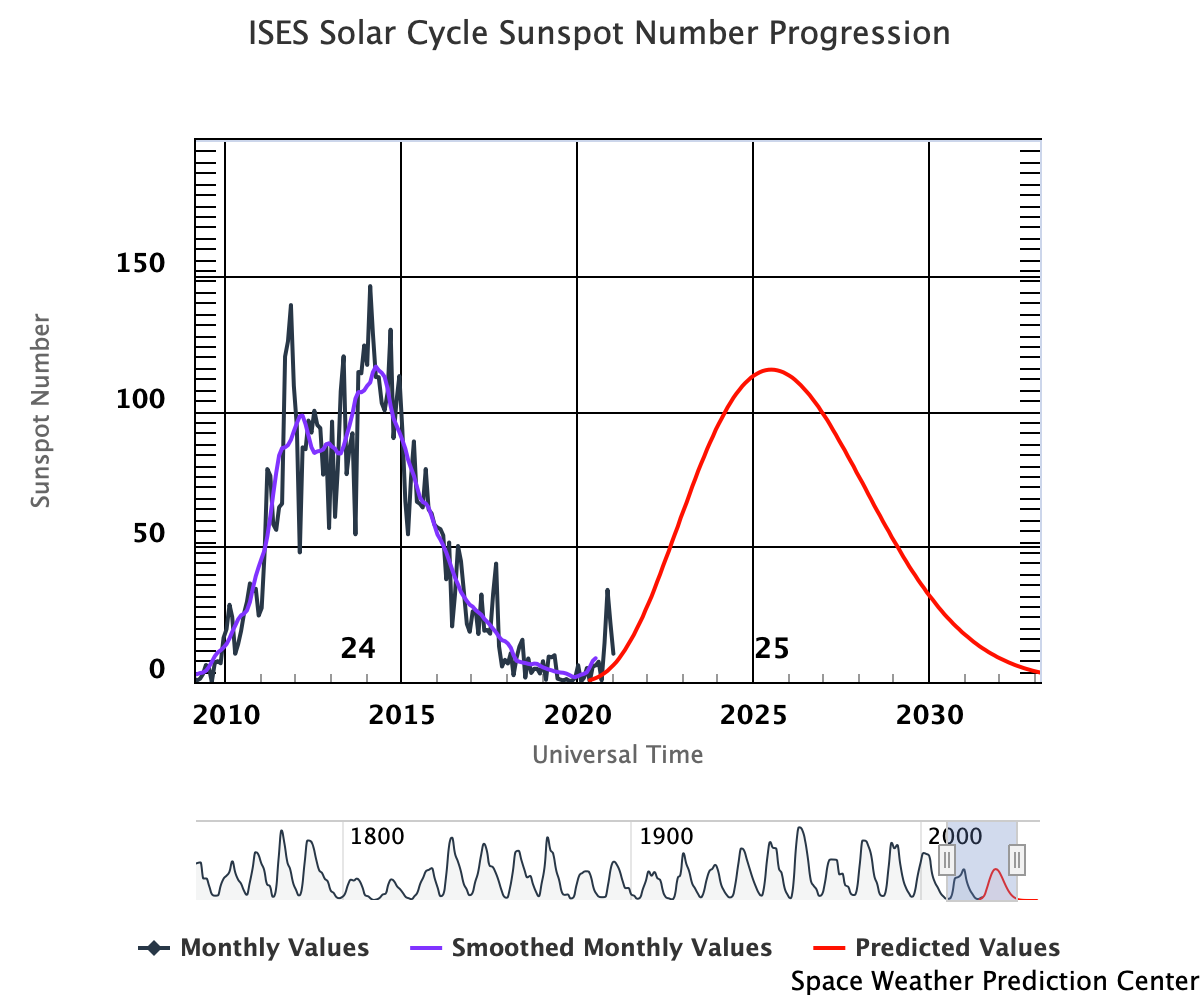
|
F10.7cm Radio Flux Progression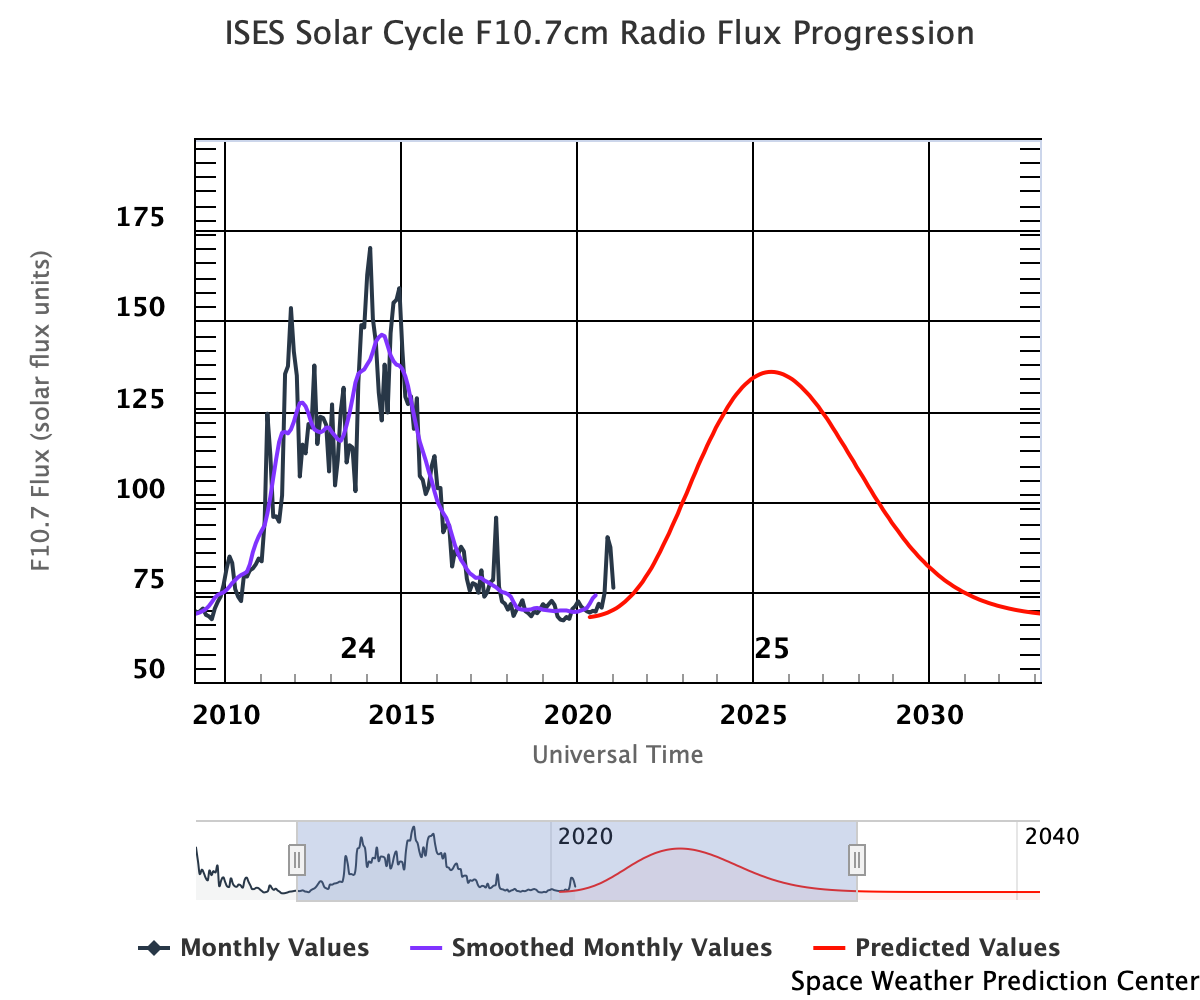
|
The Solar Cycle is observed by counting the frequency and placement of sunspots visible on the Sun. The forecast comes from the Solar Cycle Prediction Panel representing NOAA, NASA and the International Space Environmental Services (ISES). The Prediction Panel has predicted Cycle 25 to reach a maximum of 115 occurring in July, 2025.
Radio Communications Impact
D-Region Absorption
D-Region Absorption Prediction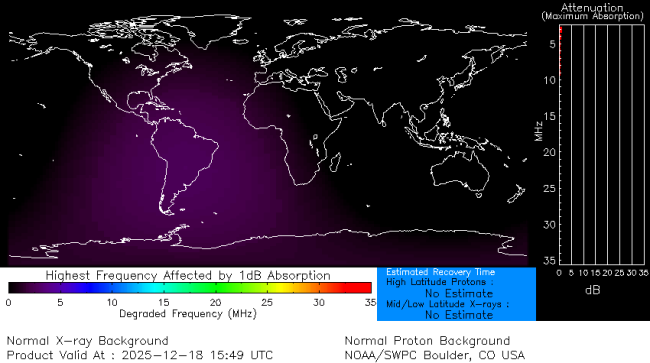
|
The D-Region Absorption Product addresses the operational impact of the solar X-ray flux and SEP events on HF radio communication. Long-range communications using high frequency (HF) radio waves (3 - 30 MHz) depend on reflection of the signals in the ionosphere. Radio waves are typically reflected near the peak of the F2 layer (~300 km altitude), but along the path to the F2 peak and back the radio wave signal suffers attenuation due to absorption by the intervening ionosphere. The D-Region Absorption Prediction model is used as guidance to understand the HF radio degradation and blackouts this can cause.
VHF and HF Band Conditions
|
|
|
Credits:
Space Weather Images and Information (excluded from copyright) courtesy of:NOAA / NWS Space Weather Prediction Center
Mauna Loa Solar Observatory (HAO/NCAR)
SOHO (ESA & NASA).
Space Weather links:
3-Day Forecast of Solar and Geophysical Activity
Space Weather Overview
LASCO Coronagraph
Real-Time Solar Wind
Space Weather Advisory Outlooks
Space Weather Forecast Disussions
Space Weather Alerts, Watches and Warnings
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)
The Very Latest SOHO Images
Powered by Space Weather PHP script by Mike Challis
additions by Martin of Hebrides Weather and Ken True of Saratoga Weather
with 3-day Solar-Geophysical Forecast text formatting by Jeremy Dyde of Jerbils Weather